In this tutorial we’ll see how to create your first Spring Boot Hello World web application using Eclipse and Maven.
Creating Maven project
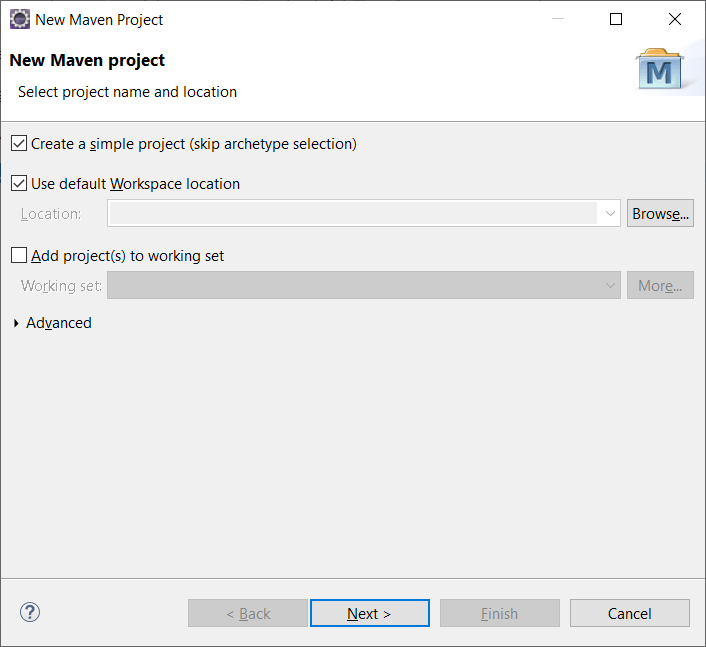
In Eclipse select File-New-Maven Project to create a Maven project.
In the “New Maven Project” window check “Create a simple project (skip archetype selection)” and click Next.
In the next window provide Group Id and Artifact Id values and click Finish.
- GroupId- This is an Id of project's group. This ID uniquely identifies the group that may have many sub-projects. For example com.knpcode.spring may contain other projects related to Spring.
- ArtifactId- This is an Id of the project. This ID uniquely identifies a project, for example SpringXML. GroupId + ArtifactId defines the artifact's location with in the repository for example com.knpcode.spring.SpringXML
That will create a Maven project structure. You may need to change the Java version as Maven Project may add Java SE5 as default, you can do it using build path property or add it in the pom.xml while adding Spring Boot dependencies. Note that Spring Boot 3.x requires Java 17 as a minimum Java version so ensure that you have at least that version of Java installed.
If you are adding Java version in the properties section of pom.xml then right click your project and select Maven-Update project to update Java version for your project.
Adding Spring Boot dependencies
Open the created pom.xml to add dependencies related to Spring Boot so that the modified pom.xml looks as given below-
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.knpcode</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootProject</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringBootProject</name>
<description>SpringBootProject</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
<relativePath />
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
- First starter that is added in the parent section of the POM is a special starter spring-boot-starter-parent that provides useful Maven defaults. This parent starter also provides a dependency-management section so that you don't need to provide version tags for dependencies. Each release of Spring Boot provides a curated list of dependencies that it supports. You don't need to provide version for any of these dependencies in your build configuration, as Spring Boot manages that for you. Note that You can still specify a version and override Spring Boot’s recommendations if you need to do so. In our configuration, Spring Boot version is 3.2.4 so Spring Boot gets the dependencies which support this version.
- Since we are developing a web application, we add a spring-boot-starter-web dependency, that adds the necessary dependencies required for creating a Spring web application.
- Third thing to add is the spring-boot-maven-plugin to our pom.xml. This plugin provides many convenient features-
- It helps to create an executable jar (über-jar), which makes it more convenient to execute and transport your service.
- It also searches for the public static void main() method to flag the class having this method as a runnable class.
With these dependencies added Spring Boot takes care of getting the required jar dependencies, even an embedded web server (Tomcat in this case) because of the starter web dependency.
Classes for web application
We’ll add a simple controller for our web application. Maven compiles sources from src/main/java so create a package at that location and add the controller in that package. I created com.knpcode.springbootproject as base package and com.knpcode.springbootproject.controller package for Controller classes.
package com.knpcode.springbootproject.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloWorldController {
@GetMapping(value="/{name}")
public String showGreeting(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
}
- Class is annotated using
@RestControllerannotation which tells Spring that this class is ready for use by Spring MVC to handle web requests and it indicates that resulting string should be written directly into the response body, we don't want to render views. - At method level
@GetMappingannotation is used which is short cut for @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET). This annotation provides routing information. It tells Spring that any HTTP request with the /{name) path should be mapped to the showGreeting method. - @PathVariable annotation lets you retrieve the parameter from the request path.
Application class with main method
Here is an application class with the components.
package com.knpcode.springbootproject;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class FirstSpringBootApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FirstSpringBootApp.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication is a convenience annotation that adds all of the following annotations-
- @Configuration annotation tags the class as a source of bean definitions for the application context.
- @EnableAutoConfiguration tells Spring Boot to enable auto configuration so that beans are created automatically based on classpath settings, other beans, and various property settings. For example starter spring-boot-starter-web adds Tomcat and Spring MVC so the auto-configuration assumes that you are developing a web application and sets up Spring accordingly which includes setting up a DispatcherServlet.
- @ComponentScan tells Spring to look recursively for other components, configurations and services inside this package and register them.
The main method is the application entry point which delegates to Spring Boot’s SpringApplication class by calling run. SpringApplication class starts Spring, which in turn, starts the embedded Tomcat web server and also bootstraps this HelloWorld application. You need to pass FirstSpringBootApp.class as an argument to the run method to tell SpringApplication which is the primary Spring component.
Running the application
You can run this Spring Boot Hello World application as a stand alone Java application or create an executable jar.
1. You can run it as a stand alone Java application by running the class with the main method (FirstSpringBootApp.java) from Eclipse IDE itself.
Right click FirstSpringBootApp.java – Run As – Java Application
2. Dependency spring-boot-starter-parent also provides a run goal that you can use to start the application. Type mvn spring-boot:run from the root project directory to start the application.
From the output on the console you can see that web server is configured, WebApplicationContext is initialized and all that is done automatically.
2019-07-19 13:26:25.989 INFO 14944 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http) 2019-07-19 13:26:26.040 INFO 14944 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat] 2019-07-19 13:26:26.042 INFO 14944 --- [ main] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/9.0.21] 2019-07-19 13:26:26.223 INFO 14944 --- [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext 2019-07-19 13:26:26.224 INFO 14944 --- [ main] o.s.web.context.ContextLoader : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 2412 ms 2019-07-19 13:26:26.589 INFO 14944 --- [ main] o.s.s.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor' 2019-07-19 13:26:26.897 INFO 14944 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path '' 2019-07-19 13:26:26.910 INFO 14944 --- [ main] com.knpcode.app.FirstSpringBootApp : Started FirstSpringBootApp in 3.83 seconds (JVM running for 16.239)
You can access the application by opening http://localhost:8080/knpCode
Here /KnpCode is the value for the name parameter.
Creating executable jar
For creating a completely self-contained executable jar file run mvn package from the command line
F:\knpcode\Spring_WorkSpace\SpringBootProject>mvn package [INFO] Scanning for projects... [INFO] [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Building SpringBootProject 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] --- maven-jar-plugin:3.1.2:jar (default-jar) @ SpringBootProject --- [INFO] Building jar: F:\knpcode\Spring_WorkSpace\SpringBootProject\target\SpringBootProject-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar [INFO]
To run application using the created jar, use the java -jar command, as follows-
java -jar target\SpringBootProject-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
That's all for the topic Spring Boot Hello World Application. If something is missing or you have something to share about the topic please write a comment.
You may also like
- Spring Boot Example Using Spring Tool Suite (STS)
- Spring Boot Stand Alone (non web) Application Example
- Spring Boot Application Using Spring Initializr
- Fail-fast And Fail-safe Iterators in Java
- Java Program to Find Maximum And Minimum Values in an Array
- PriorityBlockingQueue in Java With Examples
- Search String in Another String in Java - indexOf, lastIndexOf, contains methods
- UnsupportedClassVersionError in Java and Resolution
- React Example - Remove Object From an Array of Objects
- Uber Task in YARN